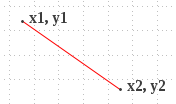graphics.eh
Graphical context for low-level drawing. More...
Constants
Types
Functions
def Graphics.copy_area(xsrc: Int, ysrc: Int, w: Int, h: Int, xdst: Int, ydst: Int);
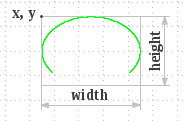
def Graphics.draw_arc(x: Int, y: Int, w: Int, h: Int, startangle: Int, arcangle: Int);
def Graphics.draw_image(im: Image, x: Int, y: Int);
def Graphics.draw_line(x1: Int, y1: Int, x2: Int, y2: Int);
def Graphics.draw_rect(x: Int, y: Int, w: Int, h: Int);
def Graphics.draw_region(im: Image, xsrc: Int, ysrc: Int, w: Int, h: Int, trans: Int, xdst: Int, ydst: Int);
def Graphics.draw_rgb(rgb: [Int], ofs: Int, scanlen: Int, x: Int, y: Int, w: Int, h: Int, alpha: Bool);
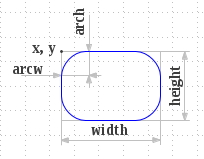
def Graphics.draw_roundrect(x: Int, y: Int, w: Int, h: Int, arcw: Int, arch: Int);
def Graphics.draw_string(str: String, x: Int, y: Int);
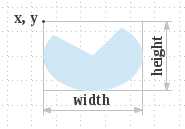
def Graphics.fill_arc(x: Int, y: Int, w: Int, h: Int, startangle: Int, arcangle: Int);
def Graphics.fill_rect(x: Int, y: Int, w: Int, h: Int);
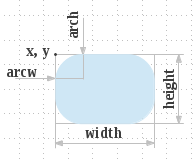
def Graphics.fill_roundrect(x: Int, y: Int, w: Int, h: Int, arcw: Int, arch: Int);
def Graphics.fill_triangle(x1: Int, y1: Int, x2: Int, y2: Int, x3: Int, y3: Int);
def Graphics.get_color(): Int;
def Graphics.get_font(): Int;
def Graphics.get_stroke(): Int;
def Graphics.set_color(rgb: Int);
def Graphics.set_font(font: Int);
def Graphics.set_stroke(stroke: Int);
|
Description
Type
Graphics represents graphical context which can be rendered
both on the display and to the offscreen images. Drawing primitives are
provided for text, images, lines, rectangles, rounded rectangles, and arcs.
Rectangles and arcs may also be filled with a solid color.
All drawing operations are performed with the current color of graphics.
New color is set with set_color function in form of
0x00RRGGBB. You can specify color by its components using expression
(red<<16)|(green<<8)|blue where red, green and blue
are numbers in range 0..255.
Line drawing operations are performed with the current stroke style of graphics.
New stroke style is set by set_stroke and may be
SOLID or DOTTED. Stroke style does not affect fill_*
functions, images or text.
Strings are rendered with the current font of graphics. New font is set by
set_font. Font constants and functions are defined
in font.eh.
Constant details
Constant for the solid stroke style.
Constant for the dotted stroke style.
No transformation applied.
Image is rotated clockwise by 90 degrees.
Image is rotated clockwise by 180 degrees.
Image is rotated clockwise by 270 degrees.
Image is mirrored horizontally.
const TR_HMIRROR_ROT90 = 7 |
Image is mirrored horizontally and then rotated clockwise by 90 degrees.
Image is mirrored vertically.
const TR_VMIRROR_ROT90 = 4 |
Image is mirrored vertically and then rotated clockwise by 90 degrees.
Type details
Graphical context to draw on.
Function details
def Graphics.get_color(): Int;
|
Returns current color to render with.
Color is returned as
0x00RRGGBB value.
def Graphics.set_color(rgb: Int);
|
Sets color used to draw new primitives.
Color is specified in form of
0x00RRGGBB.
def Graphics.get_stroke(): Int;
|
Returns the stroke style used for drawing operations.
def Graphics.set_stroke(stroke: Int);
|
Sets the stroke style used for drawing lines, arcs, rectangles, and rounded rectangles.
This does not affect fill, text, and image operations.
The value of
stroke must be one of
SOLID,
DOTTED.
def Graphics.get_font(): Int;
|
Returns current font to render strings with.
def Graphics.set_font(font: Int);
|
Sets new font to render new strings with.
Draws a line between the coordinates (
x1,
y1) and (
x2,
y2) using the current color and stroke style.
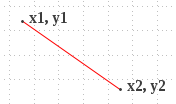
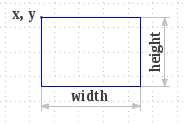
Draws the outline of the specified rectangle using the current color and stroke style.
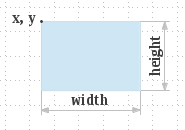
Fills the specified rectangle with the current color.
Draws the outline of the specified rounded corner rectangle using the current color and stroke style.
Fills the specified rounded corner rectangle with the current color.
Draws the outline of a circular or elliptical arc covering the specified rectangle, using the current color and stroke style.
The resulting arc begins at
startangle and extends for
arcangle
degrees. Angles are interpreted such that 0 degrees is at the 3 o'clock position.
A positive value indicates a counter-clockwise rotation while
a negative value indicates a clockwise rotation.
Fills a circular or elliptical arc covering the specified rectangle.
The resulting arc begins at
startangle and extends for
arcangle
degrees. Angles are interpreted such that 0 degrees is at the 3 o'clock position.
A positive value indicates a counter-clockwise rotation while a negative value
indicates a clockwise rotation. The filled region consists of the "pie wedge" region
bounded by the arc segment as if drawn by
draw_arc(), the radius extending
from the center to this arc at
startangle degrees, and radius extending from
the center to this arc at
startangle+
arcangle degrees.
Fills the specified triangle will the current color.
The lines connecting each pair of points are included in the filled triangle.
Draws the specified string using the current font and color.
The width and height of the rendered string may be obtained using
font_height and
str_width functions with current drawing font.
Draws specified image to the given location.
Renders an ARGB pixel data to the given location.
Pixels are stored as 24-bit color with 8-bit alpha channel in form
0xAARRGGBB.
The first pixel is stored at the specified
offset. The
scanlen
specifies the relative offset within the array between the corresponding pixels
of consecutive rows. Any value for
scanlen is acceptable (even negative
values) provided that all resulting references are within the bounds of the
array. The ARGB data is rasterized horizontally from left to right within each
row. The ARGB values are rendered in the region specified by
x,
y,
width and
height.
If alpha is false, then transparency is not processed and all values
are assumed to be fully opaque.
Copies the contents of a rectangular area (
xsrc,
ysrc,
width,
height) in given graphics to a destination area,
whose top left angle is located at (
xdest,
ydest).
Draws a region of the specified source image to the given location, possibly transforming (rotating and reflecting) the image data using the chosen transformation.
The transformation is one of
TR_* constants.